Network Traffic Models
Traffic flow is an important consideration when designing scalable, efficient
networks. Fundamentally, this involves understanding two things:
• Where do resources reside?
• Where do the users reside that access those resources?
Legacy networks adhered to the 80/20 design, which dictated that:
• 80 percent of traffic should remain on the local network.
• 20 percent of traffic should be routed to a remote network.
To accommodate this design practice, resources were placed as close as
possible to the users that required them. This allowed the majority of traffic
to be switched, instead of routed, which reduced latency in legacy networks.
The 80/20 design allowed VLANs to be trunked across the entire campus
network, a concept known as end-to-end VLANs:
End-to-end VLANs allow a host to exist anywhere on the campus network,
while maintaining Layer-2 connectivity to its resources.
However, this flat design poses numerous challenges for scalability and
performance:
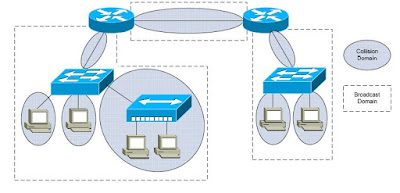
• STP domains are very large, which may result in instability or
convergence issues.
• Broadcasts proliferate throughout the entire campus network.
• Maintaining end-to-end VLANs adds administrative overhead.
• Troubleshooting issues can be difficult.
As network technology improved, centralization of resources became the
dominant trend. Modern networks adhere to the 20/80 design:
• 20 percent of traffic should remain on the local network.
• 80 percent of traffic should be routed to a remote network.
Instead of placing workgroup resources in every local network, most
organizations centralize resources into a datacenter environment. Layer-3
switching allows users to access these resources with minimal latency.
The 20/80 design encourages a local VLAN approach. VLANs should stay
localized to a single switch or switch block:
This design provides several benefits:
• STP domains are limited, reducing the risk of convergence issues.
• Broadcast traffic is isolated within smaller broadcast domains.
• Simpler, hierarchical design improves scalability and performance.
• Troubleshooting issues is typically easier.
There are nearly no drawbacks to this design, outside of a legacy application
requiring Layer-2 connectivity between users and resources. In that scenario,
it’s time to invest in a better application.
The Cisco Hierarchical Network Model
Traffic flow is an important consideration when designing scalable, efficient
networks. Fundamentally, this involves understanding two things:
• Where do resources reside?
• Where do the users reside that access those resources?
Legacy networks adhered to the 80/20 design, which dictated that:
• 80 percent of traffic should remain on the local network.
• 20 percent of traffic should be routed to a remote network.
To accommodate this design practice, resources were placed as close as
possible to the users that required them. This allowed the majority of traffic
to be switched, instead of routed, which reduced latency in legacy networks.
The 80/20 design allowed VLANs to be trunked across the entire campus
network, a concept known as end-to-end VLANs:
End-to-end VLANs allow a host to exist anywhere on the campus network,
while maintaining Layer-2 connectivity to its resources.
However, this flat design poses numerous challenges for scalability and
performance:
• STP domains are very large, which may result in instability or
convergence issues.
• Broadcasts proliferate throughout the entire campus network.
• Maintaining end-to-end VLANs adds administrative overhead.
• Troubleshooting issues can be difficult.
As network technology improved, centralization of resources became the
dominant trend. Modern networks adhere to the 20/80 design:
• 20 percent of traffic should remain on the local network.
• 80 percent of traffic should be routed to a remote network.
Instead of placing workgroup resources in every local network, most
organizations centralize resources into a datacenter environment. Layer-3
switching allows users to access these resources with minimal latency.
The 20/80 design encourages a local VLAN approach. VLANs should stay
localized to a single switch or switch block:
This design provides several benefits:
• STP domains are limited, reducing the risk of convergence issues.
• Broadcast traffic is isolated within smaller broadcast domains.
• Simpler, hierarchical design improves scalability and performance.
• Troubleshooting issues is typically easier.
There are nearly no drawbacks to this design, outside of a legacy application
requiring Layer-2 connectivity between users and resources. In that scenario,
it’s time to invest in a better application.
The Cisco Hierarchical Network Model